From March 27 to 28, 2025, The Government of France hosted the 2025 Nutrition for Growth (N4G) Summit in Paris. The N4G Summit is an international conference dedicated to defeating all forms of malnutrition by bringing together governments, international organisations, philanthropies, businesses, NGOs and other key stakeholders. Its objectives are to elevate nutrition as a key priority on the global development agenda and secure concrete political and financial commitments to accelerate progress against malnutrition.
In alignment with its mission to enhance nutrition outcomes by improving the consumption of nutritious and safe food for all people, GAIN registered two new commitments under the Nutrition Accountability Framework (NAF) to ensure accountability in achieving its objectives. These commitments build upon those that GAIN initially registered at the 2021 Tokyo N4G Summit.
On March 27th and 28th, 2025, France hosted the Nutrition for Growth Summit (N4G) in Paris. Launched in 2013 in London, N4G is a flagship international conference aimed at securing concrete political and financial commitments to combat malnutrition in all its forms. N4G brings together governments, international organisations, philanthropies, businesses, NGOs and other key stakeholders at a global and regional level to elevate nutrition as a key development agenda and accelerate progress against malnutrition.In preparation for the 2025 Nutrition for Growth (N4G) Summit, The Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) in collaboration with The Scaling Up Nutrition (SUN) Movement, the Ministry of Health of Kenya, and other stakeholders, hosted several dialogues over the past months bringing together participants representing a diverse array of sectors, including civil society organizations, private sector (e.g. food production businesses), policy-makers and media. The primary objective was to mobilize and inspire Kenyan government representatives to review and develop Kenya's commitments for the 2025 N4G Summit while reflecting on the commitments it made as a nation during the 2021 Summit.
On March 27th and 28th, 2025, France hosted the Nutrition for Growth Summit (N4G) in Paris. Launched in 2013 in London, N4G is a flagship international conference aimed at securing concrete political and financial commitments to combat malnutrition in all its forms. N4G brings together governments, international organisations, philanthropies, businesses, NGOs and other key stakeholders at a global and regional level to elevate nutrition as a key development agenda and accelerate progress against malnutrition. In preparation for the 2025 Nutrition for Growth (N4G) Summit, the Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) and the Civil Society Scaling Up Nutrition in Nigeria (CS-SUNN) hosted a Stakeholder Nutrition Dialogue in Nigeria to support the Government of Nigeria in defining the commitments to be presented at the upcoming summit.
On March 27th and 28th, 2025, France hosted the Nutrition for Growth Summit (N4G) in Paris. Launched in 2013 in London, N4G is a flagship international conference aimed at securing concrete political and financial commitments to combat malnutrition in all its forms.
N4G brings together governments, international organisations, philanthropies, businesses, NGOs and other key stakeholders at a global and regional level to elevate nutrition as a key development agenda and accelerate progress against malnutrition. In preparation for the upcoming 2025 N4G Summit, the Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) hosted two nutrition dialogues in Pakistan to help raise awareness on the N4G Summit and mobilize public and private sector actors to help address malnutrition.
In a significant step towards addressing malnutrition, the United Nations adopted Minimum Dietary Diversity as a Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) indicator. Globally, almost 3 billion people are unable to access and afford a healthy diet. Micronutrient deficiencies, caused in large part by inadequate diets is one of the leading factors in malnutrition globally. Poor diets also account for a global rise in non-communicable diseases and contribute significantly to premature mortality, worldwide.
Despite the central importance of healthy diets, until recently, global efforts towards addressing malnutrition lacked standardised metrics to effectively track diet quality. The adoption of Minimum Dietary Diversity in the SDG framework will now give governments, policy makers and international organisations a key tool to formulate evidence-based strategies that can improve diets and help reduce malnutrition.
Packaging can keep foods safe; help make them appealing, convenient, and long-lasting; and convey key information about them to consumers. At the same time, packaging is an important contributor to food system waste and a major driver of certain foods’ prices in LMICs. As such, it is a sector ripe for creative disruption as part of food system transformation – to ensure safe, nutritious foods can reach the consumers who need them, in affordable forms and with limited negative environmental impact. This paper has considered in detail three packaging innovations that could be used to make nutritious foods more accessible to lower-income consumers: single-serve packaging, reusable packaging, and selling products in bulk without individual packaging.
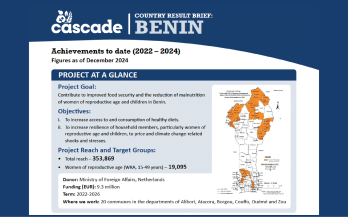
Project Description CASCADE Benin works to support and strengthen national nutrition policies in 20 communes in six of the country’s 12 departments. Implemented by CARE and GAIN in partnership with nine local organizations, the project aligns with the priorities identified in Benin’s National Food and Nutrition Policy (Politique Nationale de l’Alimentation et de la Nutrition (PNAN).
The CAtalyzing Strengthened policy aCtion for heAlthy Diets and resiliencE (CASCADE) focuses on improving nutrition and food security by promoting healthier diets through multisectoral collaboration and evidencebased food and nutrition-related policies.
Project Description
In Uganda approximately 29% and 53% of children below the age of five years are stunted and anemic, respectively. Additionally, one-third (32%) of women aged 15-49 years are anemic. Access to and consumption of healthy diets remains a challenge for women and children